1. permutation
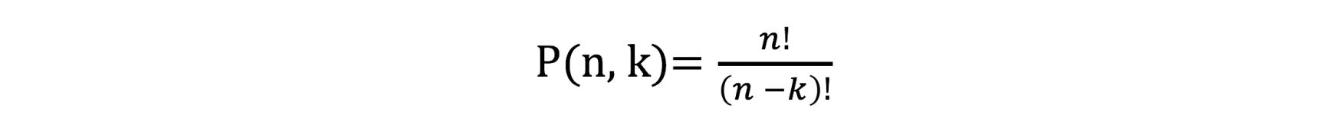
Code implement:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public class Permutation {
// n = nums.length
// P(n, k)
public static void P(int[] nums, int d, int k, boolean[] used, List<Integer> cur, List<List<Integer>> res) {
if (d == k) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(cur));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (used[i]) {
continue;
}
cur.add(nums[i]);
used[i] = true;
P(nums, d + 1, k, used, cur, res);
cur.remove(cur.size() - 1);
used[i] = false;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] testNums = new int[]{1,2,3};
boolean[] used = new boolean[testNums.length];
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
P(testNums, 0, 2, used, new ArrayList<>(), res);
for (List<Integer> item : res) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(item.toArray()));
}
}
}
Output:
[1, 2]
[1, 3]
[2, 1]
[2, 3]
[3, 1]
[3, 2]
2. combination
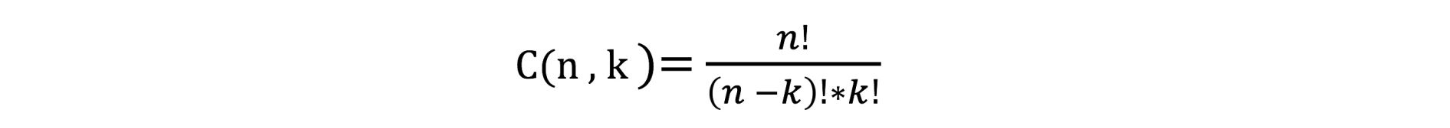
Code implement:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public class Combination {
// n = nums.length
// C(n, k)
public static void C(int[] nums, int d, int k, int start, List<Integer> cur, List<List<Integer>> res) {
if (d == k) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(cur));
return;
}
for (int i = start; i < nums.length; i++) {
cur.add(nums[i]);
C(nums, d + 1, k, i + 1, cur, res);
cur.remove(cur.size() - 1);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] testNums = new int[]{1,2,3};
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
C(testNums, 0, 2, 0, new ArrayList<>(), res);
for (List<Integer> item : res) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(item.toArray()));
}
}
}
Output:
[1, 2]
[1, 3]
[2, 3]