1. 概述
libra-wallet是libra的钱包模块,模块位置:client/libra_wallet.
libra-wallet是一个分层确定性钱包。什么是分层确定性钱包可以参考博客:数字货币确定性钱包。
其助记词参考的是比特币的BIP39,而秘钥派生以及分层钱包的设计则是参考的比特币的BIP32。与比特币的主要区别是:比特币使用基于椭圆曲线加密的椭圆曲线数字签名算法(ECDSA),特定的椭圆曲线称为secp256k1;而Libra使用的是基于Curve25519椭圆曲线的Ed25519爱德华曲线(Edwards Curve)数字签名。所以Libra对CKD(Child key derivation)做了调整,实现了自己的KDF(Key Derivation Function)。
2. 钱包架构
目前libra-wallet作为client一部分,提供账户创建、导入、导出的功能,如下图所示:
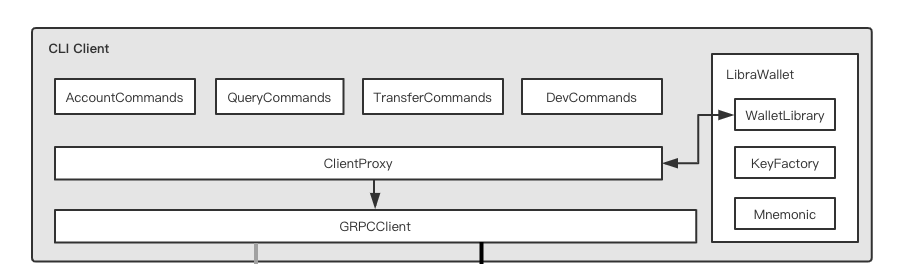
libra-wallet一共有三个关键模块:
WalletLibrary:libra钱包实例,对外提供钱包的所有功能,导入、导出、生成新账户等、KeyFactory:实现秘钥派生,基于HKDF。Mnemonic:生成助记词。
3. 钱包初始化
在client的ClientProxy初始化时,会进行钱包的初始化,如下:
impl ClientProxy {
/// Construct a new TestClient.
pub fn new(
host: &str,
ac_port: u16,
faucet_account_file: &str,
sync_on_wallet_recovery: bool,
faucet_server: Option<String>,
mnemonic_file: Option<String>,
waypoint: Option<Waypoint>,
) -> Result<Self> {
let mut client = GRPCClient::new(host, ac_port, waypoint)?;
.....
Ok(ClientProxy {
client,
accounts,
address_to_ref_id,
faucet_server,
faucet_account,
wallet: Self::get_libra_wallet(mnemonic_file)?, // 初始化钱包
sync_on_wallet_recovery,
temp_files: vec![],
})
}
// 如果没有指定mnemonic_file,初始化钱包
// 如果指定了mnemonic_file,则从中恢复钱包
fn get_libra_wallet(mnemonic_file: Option<String>) -> Result<WalletLibrary> {
let wallet_recovery_file_path = if let Some(input_mnemonic_word) = mnemonic_file {
Path::new(&input_mnemonic_word).to_path_buf()
} else {
let mut file_path = std::env::current_dir()?;
file_path.push(CLIENT_WALLET_MNEMONIC_FILE);
file_path
};
let wallet = if let Ok(recovered_wallet) = io_utils::recover(&wallet_recovery_file_path) {
recovered_wallet
} else {
let new_wallet = WalletLibrary::new(); // WalletLibrary初始化
new_wallet.write_recovery(&wallet_recovery_file_path)?;
new_wallet
};
Ok(wallet)
}
}
下面看下钱包的WalletLibrary的初始化:
impl WalletLibrary {
/// Constructor that generates a Mnemonic from OS randomness and subsequently instantiates an
/// empty WalletLibrary from that Mnemonic
#[allow(clippy::new_without_default)]
pub fn new() -> Self {
let mut rng = EntropyRng::new();
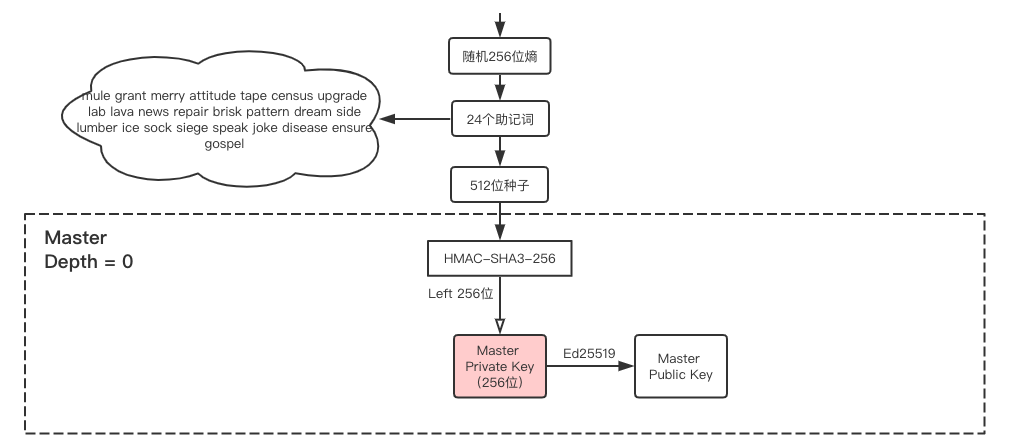
let data: [u8; 32] = rng.gen(); // 256位随机熵
let mnemonic = Mnemonic::mnemonic(&data).unwrap(); // 生成24个助记词
Self::new_from_mnemonic(mnemonic)
}
/// Constructor that instantiates a new WalletLibrary from Mnemonic
pub fn new_from_mnemonic(mnemonic: Mnemonic) -> Self {
let seed = Seed::new(&mnemonic, "LIBRA"); // 生成种子
WalletLibrary {
mnemonic,
key_factory: KeyFactory::new(&seed).unwrap(), // 初始化KeyFactory
addr_map: HashMap::new(),
key_leaf: ChildNumber(0),
}
}
}
主要做了三件事:
- 先生成256位随机熵,然后通过
Mnemonic生成24个助记词 - 通过助记词生成种子
- 通过种子初始化
KeyFactory
下面看下KeyFactory的初始化:
impl KeyFactory {
const MNEMONIC_SALT_PREFIX: &'static [u8] = b"LIBRA WALLET: mnemonic salt prefix$";
const MASTER_KEY_SALT: &'static [u8] = b"LIBRA WALLET: master key salt$";
const INFO_PREFIX: &'static [u8] = b"LIBRA WALLET: derived key$";
/// Instantiate a new KeyFactor from a Seed, where the [u8; 64] raw bytes of the Seed are used
/// to derive both the Master
pub fn new(seed: &Seed) -> Result<Self> {
let hkdf_extract = Hkdf::<Sha3_256>::extract(Some(KeyFactory::MASTER_KEY_SALT), &seed.0)?;
Ok(Self {
master: Master::from(&hkdf_extract[..32]),
})
}
}
在KeyFactory初始化时,通过Hkdf,生成了master private key。
Hkdf主要做的就是对种子做HMAC-SHA3-256,然后取左边的256位作为master private key、
整个过程如下所示:
4. 钱包导入、导出
钱包导入导出的功能比较简单:
impl WalletLibrary {
/// Function that writes the wallet Mnemonic to file
/// NOTE: This is not secure, and in general the Mnemonic would need to be decrypted before it
/// can be written to file; otherwise the encrypted Mnemonic should be written to file
pub fn write_recovery(&self, output_file_path: &Path) -> Result<()> {
io_utils::write_recovery(&self, &output_file_path)?;
Ok(())
}
/// Recover wallet from input_file_path
pub fn recover(input_file_path: &Path) -> Result<WalletLibrary> {
let wallet = io_utils::recover(&input_file_path)?;
Ok(wallet)
}
}
导入导出的实现在io_utils中:
/// Recover wallet from the path specified.
pub fn recover<P: AsRef<Path>>(path: &P) -> Result<WalletLibrary> {
let input = File::open(path)?;
let mut buffered = BufReader::new(input);
let mut line = String::new();
let _ = buffered.read_line(&mut line)?;
let parts: Vec<&str> = line.split(DELIMITER).collect();
ensure!(parts.len() == 2, format!("Invalid entry '{}'", line));
let mnemonic = Mnemonic::from(&parts[0].to_string()[..])?;
let mut wallet = WalletLibrary::new_from_mnemonic(mnemonic);
wallet.generate_addresses(parts[1].trim().to_string().parse::<u64>()?)?;
Ok(wallet)
}
/// Write wallet seed to file.
pub fn write_recovery<P: AsRef<Path>>(wallet: &WalletLibrary, path: &P) -> Result<()> {
let mut output = File::create(path)?;
writeln!(
output,
"{}{}{}",
wallet.mnemonic().to_string(),
DELIMITER,
wallet.key_leaf()
)?;
Ok(())
}
可以看到,导出就是把助记词和ChildNumber导出到文件,文件中类似:
mule grant merry attitude tape census upgrade lab lava news repair brisk pattern dream side lumber ice sock siege speak joke disease ensure gospel;4
分号后的4就是指有4个child。
而导入,则是从助记词文件加载。
5. 秘钥派生新账户
通过WalletLibrary的new_address()从master派生新账户:
/// Function that generates a new key and adds it to the addr_map and subsequently returns the
/// AccountAddress associated to the PrivateKey, along with it's ChildNumber
pub fn new_address(&mut self) -> Result<(AccountAddress, ChildNumber)> {
let child = self.key_factory.private_child(self.key_leaf)?; // 派生下一个child
let address = child.get_address()?;
let old_key_leaf = self.key_leaf;
self.key_leaf.increment();
if self.addr_map.insert(address, old_key_leaf).is_none() {
Ok((address, old_key_leaf))
} else {
Err(WalletError::LibraWalletGeneric(
"This address is already in your wallet".to_string(),
))
}
}
秘钥派生新账户实现在KeyFactory的private_child()中:
/// Derive a particular PrivateKey at a certain ChildNumber
///
/// Note that the function below adheres to [HKDF RFC 5869](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc5869).
pub fn private_child(&self, child: ChildNumber) -> Result<ExtendedPrivKey> {
// application info in the HKDF context is defined as Libra derived key$child_number.
let mut le_n = [0u8; 8];
LittleEndian::write_u64(&mut le_n, child.0);
let mut info = KeyFactory::INFO_PREFIX.to_vec();
info.extend_from_slice(&le_n);
let hkdf_expand = Hkdf::<Sha3_256>::expand(&self.master(), Some(&info), 32)?;
let sk = Ed25519PrivateKey::try_from(hkdf_expand.as_slice())
.expect("Unable to convert into private key");
Ok(ExtendedPrivKey::new(child, sk))
}
可以看到Libra只实现了从matser的私钥派生child,派生只需要master priv key 和 ChildNumber,而KDF的具体实现在crypto/crypto/src/hkdf.rs中,这是是Libra对HKDF(HMAC-based Extract-and-Expand Key Derivation Function)的实现,这边不展开了。
6. 总结
综上,Libra的分层确定性钱包如下所示:

可以看到相比比特币,Libra实现的还是比较简单的,CKD只实现了Private parent key → private child key,只有master和child两层。